Analysing Scientific Publications Using AI
Thesis Type |
|
Student |
Philipp Hertweck |
Status |
Finished |
Proposal on |
27/02/2024 10:30 am |
Proposal room |
Seminar room I5 6202 |
Presentation on |
20/09/2024 2:00 pm |
Presentation room |
Seminar room I5 6202 |
Supervisor(s) |
Stefan Decker |
Advisor(s) |
Sulayman K. Sowe Yongli Mou Alexander Neumann |
Contact |
sowe@dbis.rwth-aachen.de mou@dbis.rwth-aachen.de neumann@dbis.rwth-aachen.de |
Scientific publications analysis, a special kind of Document Analysis (DA), is the quantitative and qualitative analysis of the content of a publication with the sole purpose of making more sense of the written content, generating more insights beyond the abstract and making the publication document more understandable to readers.
The main goal of the thesis project is to develop the expertise and tools needed to extract, summarise and analyse scientific publications written in LaTeX.
The proposed thesis project research methodology (Figure below) shows that the candidate will review LaTeX source scientific publications and apply his/her programming skills to segment the documents into manageable chunks that the LLM of an AI tool (e.g., ChatGPT, LangChain) can understand. Using a suitable LLM, she/he will generate, analyse and compile the summaries into a ‘’new’’ article for various audiences.
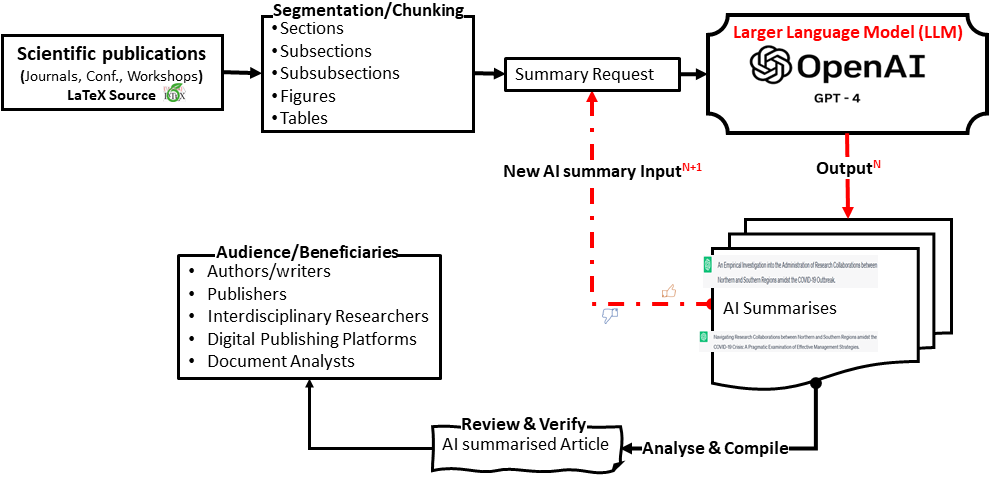
The candidate is welcome to join and get support from the DBIS/Fraunhofer FIT AI(LLM) working group to help you understand the latest LLMs R&D trends. In collaboration with your advisor, you will review and verify the outputs of the AI summaries. You are encouraged to publish your findings, tools, code, and the systems you used. Your advisor and supervisor will support you in documenting the lessons you have learnt, the research challenges you encountered, and the future research directions you plan to undertake.
Opportunities and benefits:
- Get support in learning practical skills to prepare you for the ‘’world of work’’.
- Learn to write and co-publish scientific papers with expert senior researchers and professors.
- Opportunities to continue your work as a student worker and to travel to present your research at international conferences and workshops.
- Opportunity and support to take your research to the next level (PhD).
Opportunities beyond your RWTH Thesis project:
In a world dominated by AI, the demand for computer scientists and software engineers with AI-based document analyst knowledge and expertise is limitless. For example, big companies like IBM, SAP, Dexpro.de, Deutsche Bank, and Google’s Document AI Solutions use AI to analyse various documents and workflows.
Recommended reading list:
- Bowen, G.A. (2009). Document Analysis as a Qualitative Research Method, Qualitative Research Journal, Vol. 9 No. 2, pp. 27-40. https://doi.org/10.3316/QRJ0902027
- Morgan, H. (2022). Conducting a Qualitative Document Analysis. The Qualitative Report, 27(1), 64-77. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/2022.5044
- Niful Islam, et al. (2023). Distinguishing Human Generated Text From ChatGPT Generated Text Using Machine Learning. arXiv:2306.01761v1, https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2306.01761.
- Sébastien Bubeck, et al. (2023). Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4. arXiv:2303.12712v5, https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.12712
- GeneRation Of BIbliographic Data: https://grobid.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Introduction/
- Grobid Bibliographical Extraction: http://grobid.wikidata.dbis.rwth-aachen.de/
- Pankaj Tripathi (2023). The Future Of AI-Powered Document Processing. Available at https://www.docsumo.com/blog/document-ai-future, accessed Friday, 07 July 2023.
Interested, eager to start and have fun?
Contact the thesis advisor: Dr. Sulayman K Sowe (sowe@dbis.rwth-aachen.de)
For more information, please visit: Information about Thesis Process
Flyer_AI-Based Documents Analysis using Large Language Models (LLMs)
- Programming in Python or a suitable programming language.
- Experience in using and managing GitHub repositories.
- Knowledge of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
- How to use and write documents in LaTeX.
- Text mining, Natural Language Processing, and Neural networks.
- Good reading and writing skills in German and English.
- Ability to quickly adapt to working in a large multiculturally academic environment.
